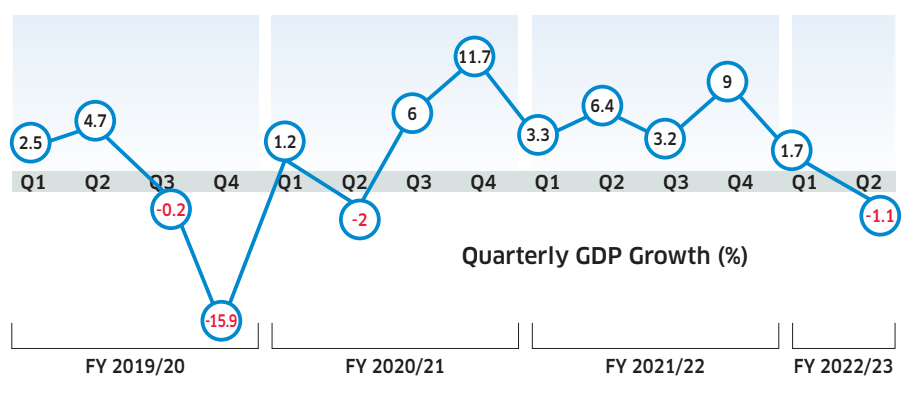
It’s official. Nepal’s economy is going through a deep recession. According to the National Statistics Office (NSO), the country’s economic growth has turned negative in the second quarter of the current fiscal year. In its economic growth projection for the second quarter, NSO said the gross domestic product (GDP) growth has been negative by 1.1 percent. GDP growth has suffered this fiscal largely due to tight monetary policy, slackened domestic demand, the unwinding of the Covid-19 stimulus, and persistent global headwinds.
With the sharp slowdown in economic activities and higher interest rates, the country’s economy has been under pressure from the start of FY 2022/23. The economy grew by a meager 1.7 percent in the first quarter of the current fiscal year. The last time when the country’s GDP turned negative was in the second quarter of FY 2020/21 when the economy was reeling under the Covid-19 pandemic. This year, the slump in the construction, mining, transport, and manufacturing sectors, and wholesale and retail trade dragged down the overall economic growth.
The NSO report shows the mining sector grew by negative 16.4 percent while the construction sector is negative by 20.6 percent. Similarly, the wholesale and retail trade’s growth turned negative by 9.7 percent while the manufacturing sector is also negative by 4.3 percent.
According to NSO, the growth of the manufacturing sector is likely to decelerate further due to higher interest rates, import restriction measures, and the slowdown in domestic consumption. A dampened external demand has affected manufacturing and construction subsectors. The mining and construction sector has been going through a prolonged slump due to a sharp decline in the demand for cement, steel, and other construction materials. The demand for cement, steel, sand, and other construction materials has decreased with construction activities in the country coming to a halt.
The decline in public construction and the downturn in private house construction have resulted in a decrease in the consumption of construction materials. The import restrictions and falling market demands have hit the wholesale and retail trade. Credit control measures and a hike in interest rates have slowed down real estate, wholesale, and retail trade activities. Experts say a negative economic growth rate indicates a grinding halt in economic activities.
Economist Chandra Mani Adhikari said the slowdown in economic activities has impacted the country's economic growth. “The government has not been able to pay more than Rs 60bn to the contractors,” said Adhikari, “This has affected the cash flow not only in the construction sector but also in industries like cement, steel, and other construction materials.”
According to Adhikari, the disruption in the cash flow has made it difficult for businesses even to repay the loans of the banks. The only silver lining is, the growth of the hotel and restaurant services sector has increased by 20.4 percent in the second quarter of this fiscal year compared to a growth of 2.2 percent in the second quarter of last fiscal year.
The NSO report is in line with the growth estimates of the World Bank (WB) and Asian Development Bank (ADB). Both WB and ADB have projected that Nepal's economic growth would grow at 4.1 percent this year.